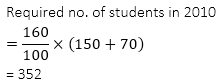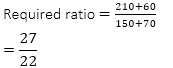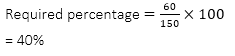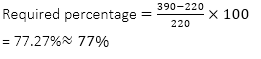Q1. रोबिन, लतिका के बाएं
बैठा है, मनोज, रमेश और लतिका के मध्य में बैठा है. यदि गोविन्द भी लतिका के बाएं है तो, बाएं छोर पर कौन बैठा है?
सकता
Q2. यदि
निकिता > ललित और राशी < निकिता तो
तो निम्नलिखित में से कौन से चिन्ह क्रमश: खाली स्थान में भरे जाने चाहिए (बाएं से दायें)?
प्रिया < राशि ≤ शशि = माया__निकिता=कविता__ललित
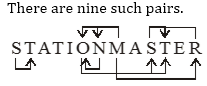
Q3. दिए गए शब्द "STATIONMASTER" ऐसे कितने वर्णों के
युग्म हैं जिनके मध्य उतने ही वर्ण हैं जितने अंग्रेजी वर्णमाला के मध्य आते हैं?
Q4. उत्तर कि ओर मुख करके खड़े बच्चों की एक पंक्ति में,
रंजन दायें छोर से बारहवां है और
सत्यार्थी के दायें से पांचवां है जो कि बाएं छोर से दसवां है. पंक्ति में कुल
कितने बच्चे हैं?
Sathyarthi’s position from right end = 17th
Total number of children in the row = 10 + 17 – 1 = 26
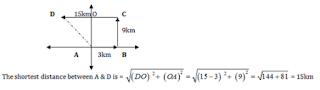
Q5. एक व्यक्ति एक बिंदु A से B तक पूर्व की ओर 3कि.मी चलता है और फिर बाएं मुड़कर C पर पहुचने के लिए उसके तीन गुना दूरी तय करता है(A और B के मध्य तय की गई दूरी). वह दोबारा बाएं मुड़ता है और D तक पहुचने के लिए A और B के मध्य तय की गई दूरी
के पांच गुना चलता है. आरंभिक बिंदु और अंतिम
बिंदु के मध्य सबसे छोटी दूरी है:
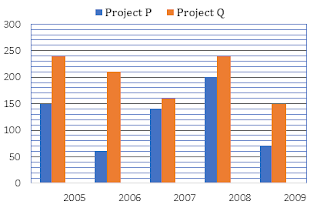
Directions (6-10): निम्नलिखित बार-चार्ट में दो परियोजनाओं P और Q में 2005 से 2009 के बीच भिन्न वर्षों में
दाखिला लेने वाले विद्यार्थियों की कुल संख्या को दर्शाया गया है, बार-चार्ट के आधार पर निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों को हल
कीजिए.
Q6. यदि वर्ष 2010 में, दोनों परियोजनाओं में 2009 में नामांकित छात्रों की कुल संख्या में 60% वृद्धि हुई है, तो 2010 में नामांकित छात्रों की कुल संख्या ज्ञात कीजिये.
Q7. दोनों परियोजनाओं में
वर्ष 2006 में छात्रों कि कुल
संख्या का वर्ष 2009 में छात्रों कि कुल
संख्या से कितना अनुपात है?
Q8. 2006 में परियोजना P के छात्रों कि संख्या 2009 में परियोजना Q के
छात्रों के कितने प्रतिशत है?
Q9. परियोजना P में 2006 से 2009 तक नामांकित छात्रों की संख्या एक साथ 2008 और 2009 में परियोजना Q में नामांकित छात्रों की तुलना में कितने प्रतिशत
अधिक है(लगभग)?
Q10. परियोजना Q में 2008 और 2009 में नामांकित छात्रों की कुल संख्या 2005 और 2009 में परियोजना P में नामांकित छात्रों की तुलना में कितने प्रतिशत
अधिक है?(लगभग)
Directions (11-15): Rearrange the following five sentences (A), (B), (C), (D) and (E) in the proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph and then answer the questions given below.
Q11. (A) A valid ‘Living Will’ facilitates passive euthanasia. A failure to legally recognize an advance medical directive inconveniences the “right to smoothen the dying process”, the court reasoned.
(B) It called passive euthanasia as a “mere acceleration of the inevitable conclusion.” Active euthanasia, the court concluded, is unlawful.
(C) In cases of terminally ill or permanently vegetative state patients, where there is no hope for revival, priority should be given to the Living Wills and the right of self-determination.
(D) Suicide involves “overt acts” which culminates in an unnatural death.
(E) The court distinguished passive euthanasia from suicide and active euthanasia.
Q12. (A) They had no idea what an elephant was, and so they decided, "Even though we will not be able to see it, we can feel it. Let's go."
(B) "Oh, no! it is like the branch of a tree," said the third man, touching the tusk of the elephant.
(C) One day the villagers were very excited, and when they asked what was happening they told them, "Hey, there is an elephant in the village today!"
(D) So, they all went to where the elephant was, and each of them touched it: "Hey, the elephant is a pillar," said the first man, touching its leg.
(E) "Oh, no! it is like a rope," said the second man, who was touching the tail.
Q13. (A) The previous winter having been unusually severe, this spring feeling was like a form of intoxication in May, as if there were an overabundant supply of sap.
(B) Everybody I met seemed to be smiling; an air of happiness appeared to pervade everything in the warm light of returning spring.
(C) One might almost have said that a breeze of love was blowing through the city, and the sight of the young women whom I saw in the streets in their morning toilets, in the depths of whose eyes there lurked a hidden tenderness, and who walked with languid grace, filled my heart with agitation.
(D) One morning on waking I saw from my window the blue sky glowing in the sun above the neighbouring houses.
(E) The canaries hanging in the windows were singing loudly, and so were the servants on every floor; a cheerful noise rose up from the streets, and I went out, my spirits as bright as the day, to go—I did not exactly know where.
Q14. (A) Sometimes he had flashbacks of sandstorms that used to whirl around the village, leaving behind a thick sandy layer all over the houses and even on his face.
(B) After settling down in the valley, he had adjusted to his new life by accepting the title of shepherd, something that he had never thought of doing before his forced immigration.
(C) Once the herd was settled, and busy grazing, he would sit down under his favourite tree and rest his head on the tree trunk and watch over the herd.
(D) It was his job to lead the herd to pasture and let them graze randomly on the lush green patches.
(E) He would often daydream of his beautiful village in Afghanistan: he missed the giant, dry mountains that stood erect like soldiers, as if they were guarding the village.
Q15. (A) The tower is 324 metres (1,063 ft) tall, about the same height as an 81-storey building, and the tallest structure in Paris. Its base is square, measuring 125 metres on each side.
(B) Constructed from 1887–89 as the entrance to the 1889 World's Fair, it was initially criticized by some of France's leading artists and intellectuals for its design, but it has become a global cultural icon of France and one of the most recognizable structures in the world.
(C) The Eiffel Tower is the most-visited paid monument in the world; 6.91 million people ascended it in 2015.
(D) The Eiffel Tower is a wrought iron lattice tower on the Champ de Mars in Paris, France.
(E) It is named after the engineer Gustave Eiffel, whose company designed and built the tower.